Diseases of crustaceans
Viral diseases—White tail disease
CLICK ON IMAGE TO ENLARGE

Source: AS Sahul Hameed
Signs of disease
Important: animals with disease may show one or more of the signs below, but disease may still be present in the absence of any signs.
Disease signs at the farm level
- Presence of whitish postlarvae, followed by mortality 2 to 3 days after the conversion of first postlarva in larval rearing tanks. Maximum mortalities around 5 days after the appearance of the first gross sign.
Clinical signs of disease in an infected animal
- Abdomen (tail) is particularly milky and opaque. Discolouration starts at the tail extremity (telson region) and gradually progresses towards the head. Eventually, all muscles in the abdomen and cephalothorax are affected.
- Affected postlarvae are more milky and opaque than unaffected postlarvae. These clinical signs are usually followed by death, with variable mortality rate up to 95%.
- The tissues most affected in moribund postlarvae and early juveniles are striated muscles of the abdomen and cephalothorax and the intratubular connective tissue of the hepatopancreas.
Disease agent
The causative agent is Macrobrachium rosenbergii Nodavirus (MrNV) and extra small virus (XSV). Both of these viruses have been found to be associated with the disease, but their respective roles are not yet clear.
Host range
Crustaceans known to be susceptible to white tail disease:
giant freshwater prawn* (Macrobrachium rosenbergii)
* naturally susceptible
Presence in Asia–Pacific
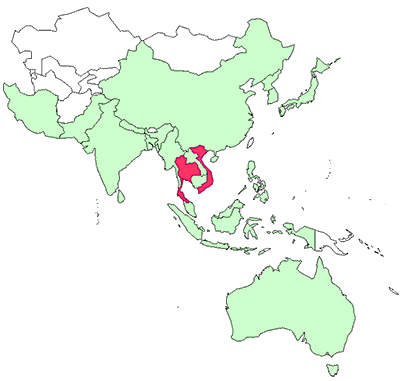
White tail disease has been officially reported from Thailand and Vietnam.
Epidemiology
- Very few postlarvae showing the clinical signs of white tail disease survive. Survivors seem to grow normally in grow-out ponds.
- Outbreaks most commonly occur in larvae, postlarvae and early juveniles. There is no evidence of adult life stages being affected, but adults might act as carriers.
- Transmission is both vertical and horizontal.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnostic table and the list of similar diseases appearing at the bottom of each disease page refer only to the diseases covered by this field guide. Gross signs observed might well be representative of a wider range of diseases not included here. Therefore, these diagnostic aids should not be read as a guide to a definitive diagnosis, but rather as a tool to help identify the listed diseases that most closely account for the gross signs.
Similar diseases
The clinical signs described and shown here may also be symptomatic of other bacterial or viral infections, or poor water quality. Further laboratory examination is needed for a definitive diagnosis.
Sample collection
Because of uncertainty in differentiating diseases using only gross signs, and because some aquatic animal disease agents might pose a risk to humans, you should not try to collect samples unless you have been trained. Instead, you should phone your national hotline number and report your observations. If samples have to be collected, the agency taking the call will advise you on what you need to do. Local or district fisheries/veterinary authorities could advise you on sampling.
Emergency disease hotline
For your national emergency disease hotline number, see Whom to contact if you suspect a disease.
Further reading
The currently accepted procedures for a conclusive diagnosis of white tail disease are summarised at
http://www.oie.int/aac/eng/cards/en_diseasecard.htm
This hyperlink was correct and functioning at the time of publication.

