Diseases of finfish
Viral diseases—Infectious haematopoietic necrosis
CLICK ON IMAGE TO ENLARGE

Source: J Fryer
CLICK ON IMAGE TO ENLARGE
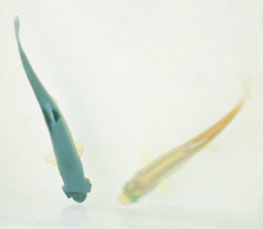
Source: G Kurath
Signs of disease
Important: animals with disease may show one or more of the signs below, but disease may still be present in the absence of any signs.
The disease signs described below are seen only in young salmonids (disease in adults is subclinical).
Disease signs at the farm level
- mass mortality in young salmonids
Disease signs at the tank or pond level
- feeble swimming action
Clinical signs of disease in an infected animal
- fry of rainbow trout and salmon show numerous yolk sac haemorrhages
- darkening of the skin
- haemorrhages on the abdomen and around pupil of eye
- occasionally exophthalmus (pop eye) and ascites (swollen abdomen from accumulated fluid)
- possible long, white discharge from anus
- bleeding at base of fins
Gross signs of disease in an infected animal
- stomach empty of food but swollen with a gelatinous substance
- pale internal organs
- petechial (pinpoint) haemorrhages in the fatty tissue and muscle surrounding organs and stomach wall
Disease agent
Infectious haematopoietic necrosis is caused by infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV), a rhabdovirus related to viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus.
Host range
Fish known to be susceptible to infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus:
amago salmon* (Oncorhynchus rhodurus)
Atlantic salmon* (Salmo salar)
brook trout* (Salvelinus fontinalis)
brown trout* (Salmo trutta)
chinook salmon* (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha)
chum salmon* (Oncorhynchus keta)
coho salmon* (Oncorhynchus kisutch)
cutthroat trout* (Salmo clarki)
masou salmon* (Oncorhynchus masou)
Pacific salmon* (Oncorhynchus spp)
pink salmon* (Oncorhynchus gorbuscha)
rainbow trout* (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
sockeye salmon* (Oncorhynchus nerka)
Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus)
gilt-head seabream (Sparus aurata)
Pacific herring (Clupea pallasii)
pike (Esox lucius)
pile perch (Damalichthys vacca)
shiner perch (Cymatogaster aggregata)
tubesnout stickleback (Aulorhynchus flavidus)
turbot (Scophthalmus maximus)
Nonpiscine carriers include:
gill lice (Salminicola spp)
leeches (Piscicola spp)
mayfly (Callibaetis sp)
* naturally susceptible (other species have been shown to be experimentally susceptible)
Presence in Asia–Pacific
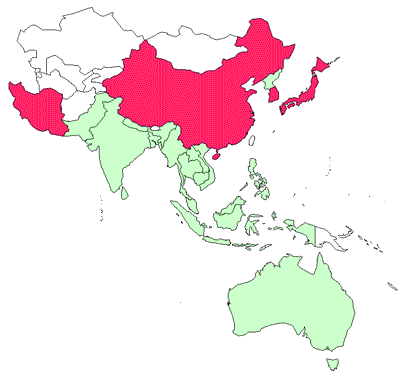
IHN has been officially reported from China, Iran, Japan and the Republic of Korea.
Epidemiology
- IHN is typically found in young farmed trout and Atlantic salmon in the fingerling stage or in the final spawning period of their lifecycle.
- Mass mortalities can occur, typically with 100% of population infected and mortality greater than 90%.
- High mortality also occurs in wild Pacific salmon infected with IHNV, and survivors can be the source of infection of farmed stock.
- Susceptibility to overt infection varies between individuals of the same species and appears to be largely age dependent, with younger individuals being more susceptible.
- Fish that survive IHN are presumed to be carriers of the virus.
- Transmission is generally via water, with the virus entering fish through the gills and skin.
- The virus enters the water in faeces, urine, spawning fluids and external mucus, and through contaminated transport water and blood-sucking parasites of infected fish.
- Fish-eating birds can also transfer virus to new areas.
- Outbreaks are most likely to occur around spawning, with increased levels of virus excreted to water with spawning fluids.
- IHN is a cold-water disease. Outbreaks rarely occur in water above 15°C and require a neutral pH of around 7.
- It is believed the migration of IHNV from northern America to Asia and Europe has been through the importation of infected fish and eggs, indicating some degree of vertical transmission.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnostic table and the list of similar diseases appearing at the bottom of each disease page refer only to the diseases covered by this field guide. Gross signs observed might well be representative of a wider range of diseases not included here. Therefore, these diagnostic aids should not be read as a guide to a definitive diagnosis, but rather as a tool to help identify the listed diseases that most closely account for the gross signs.
Similar diseases
Viral haemorrhagic septicaemia, infectious salmon anaemia, infectious pancreatic necrosis
Sample collection
Because of uncertainty in differentiating diseases using only gross signs, and because some aquatic animal disease agents might pose a risk to humans, you should not try to collect samples unless you have been trained. Instead, you should phone your national hotline number and report your observations. If samples have to be collected, the agency taking the call will advise you on what you need to do. Local or district fisheries/veterinary authorities could advise you on sampling.
Emergency disease hotline
For your national emergency disease hotline number, see Whom to contact if you suspect a disease.
Further reading
http://www.oie.int/aac/eng/cards/en_diseasecard.htm
http://www.collabcen.net/toWeb/aq2.asp
The currently accepted procedures for a conclusive diagnosis of IHN are summarised at
http://www.oie.int/eng/normes/fmanual/A_00019.htm
These hyperlinks were correct and functioning at the time of publication.

