Diseases of crustaceans
Histological page for Infectious Hypodermal and Haematopoietic Necrosis
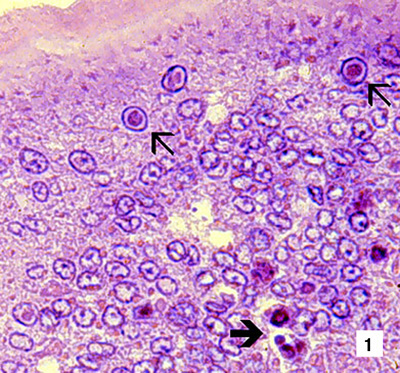 |
Low magnification (830x) photomicrograph (LM) of an H&E stained section of a juvenile blue shrimp (Penaeus stylirostris) with severe acute infectious hypodermal and haematopoietic necrosis (IHHN) disease. The section is through the cuticular epithelium and subcuticular connective tissues just dorsal and posterior to the heart. Numerous necrotic cells with pyknotic nuclei or with pathognomonic eosinophilic intranuclear inclusion bodies (Cowdry type A) are present (arrows) Source: DV Lightner |
|---|---|
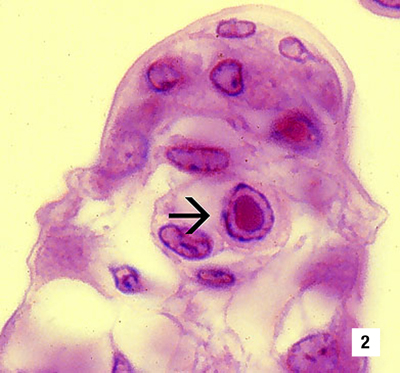 |
High magnification (1800x) LM of gills showing eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions (Cowdry type A inclusions or CAIs) that are pathognomonic for IHHNV infections Source: DV Lightner |
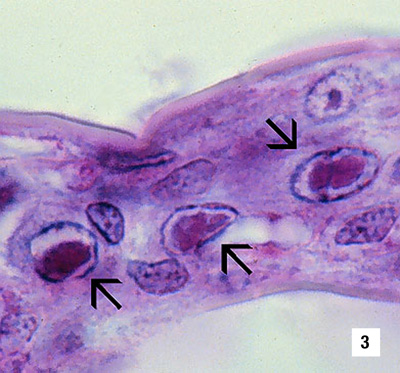 |
A high magnification (1800x) LM of a gill lamella showing three adjacent cells with diagnostic IHHN CAIs in their hypertrophied nuclei Source: DV Lightner |
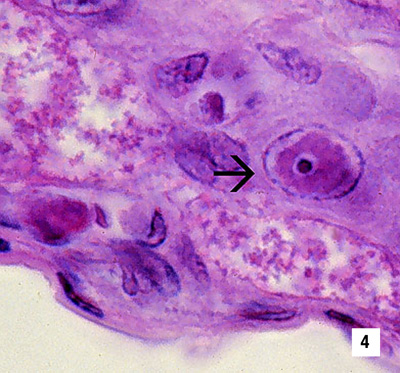 |
Another IHHNV CAI in the nucleus of a gill epithelial cell showing a chromatin process within the inclusion body (1800x) Source: DV Lightner |
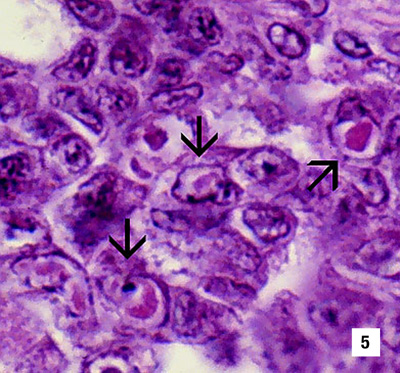 |
Section through a haematopoietic nodule showing several cells with IHHNV CAIs (1800x) Source: DV Lightner |
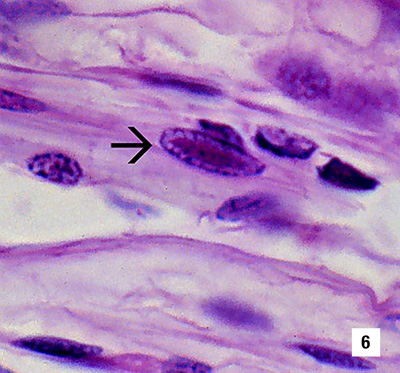 |
Mid-sagittal section of the ventral nerve cord of a juvenile white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) with runt-deformity syndrome. Note that CAIs take the shape of the host cell nucleus. Thus, in the nerve cord they often are elliptical and appear slightly different from CAIs in other tissues (1800x) Source: DV Lightner |
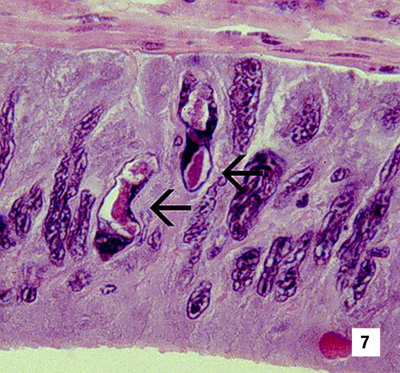 |
Section of the vas deferens of an adult P. vannamei with IHHN. Bizarrely shaped CAIs (which take the shape of the nuclei of this tissue) are illustrated (700x) Source: DV Lightner |
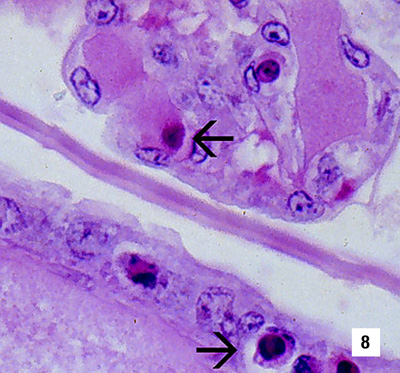 |
Section of the gills of a juvenile blue shrimp with IHHN. While necrotic cells with pyknotic nuclei are numerous, no diagnostic CAIs are apparent (700x) Source: DV Lightner |
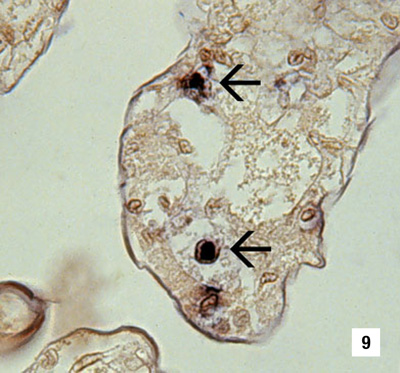 |
A section of gills has reacted with a DIG-labelled DNA gene probe for IHHNV. Several IHHNV-infected cell nuclei have reacted with the probe. Viral DNA is stained dark blue to black by the detection reaction for DIG-labelled probe. DIG-labelled probe and Bismarck Brown (700x) Source: DV Lightner |
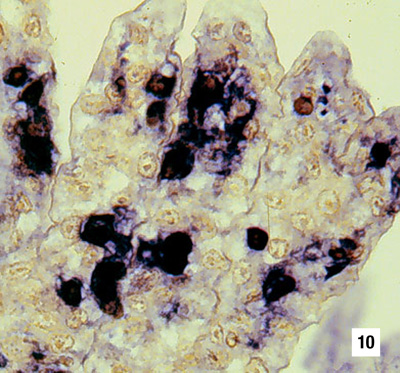 |
Section of gills from a juvenile P. stylirostris with G4 IHHN. Probe positive IHHNV-infected cells are abundant. DIG-labelled probe and Bismarck Brown (700x) Source: DV Lightner |
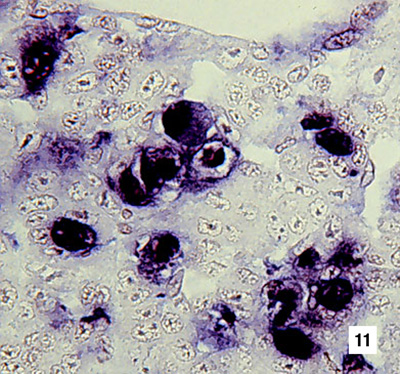 |
Section of haematopoietic tissue from a juvenile blue shrimp with Probe-positive cells are abundant. DIG-labelled probe and Bismarck Brown (700x) Source: DV Lightner |
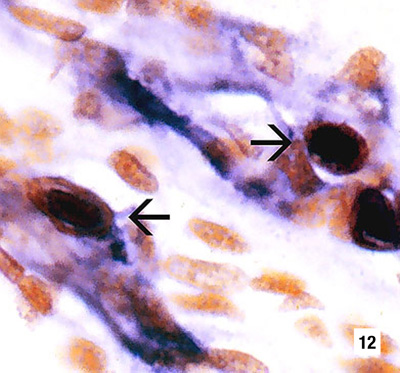 |
Mid-sagittal section from a juvenile white shrimp with runt-deformity syndrome. The probe has reacted with several CAIs and with cellular debris or haemolymph with a high content of IHHNV. DIG-labelled probe and Bismarck Brown (600x) Source: DV Lightner |

